New publication in Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
We are happy to announce that our latest publication “CineVN: Variational network reconstruction for rapid functional cardiac cine MRI” (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mrm.30260) has been published in Magnetic Resonance in Medicine!
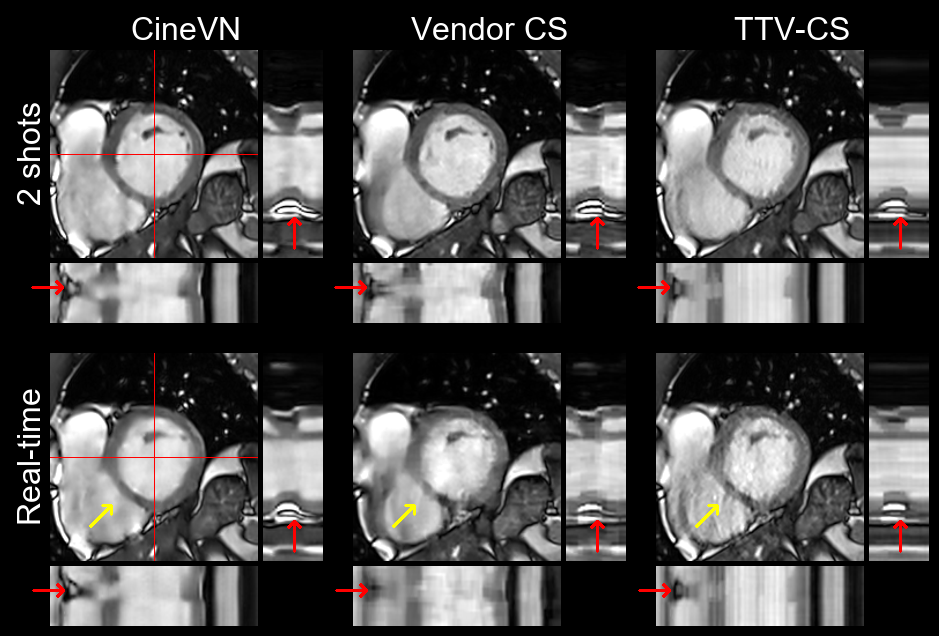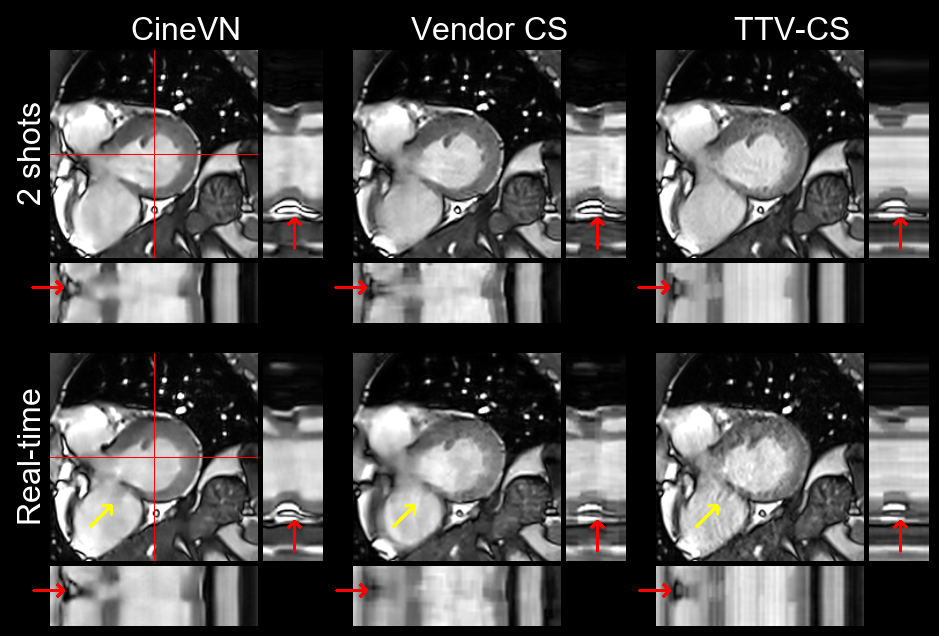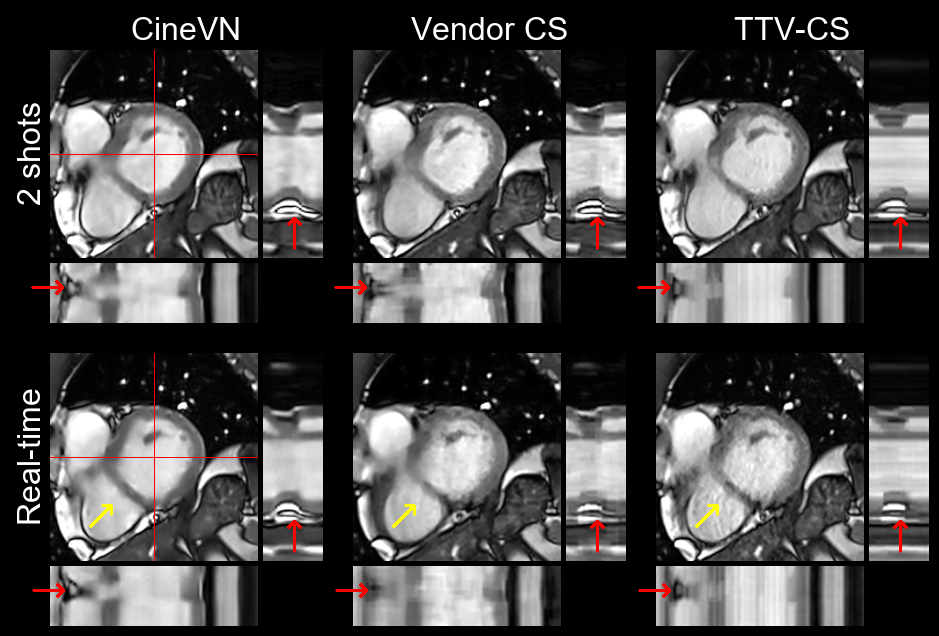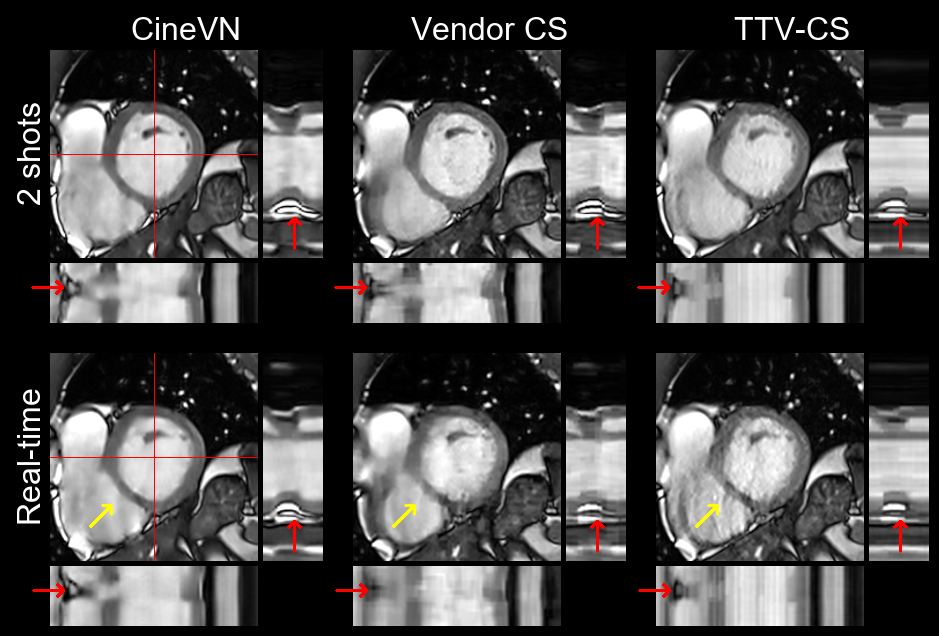
We demonstrate fast inline reconstructions of high-resolution real-time cine MRI with better image quality and more accurate evaluation of cardiac function and myocardial strain compared to state-of-the-art compressed sensing reconstructions. This research was a joint effort of the Computational Imaging Lab with Siemens Healthineers AG, MVZ Diagnostikum Berlin GmbH, and The Ohio State University.
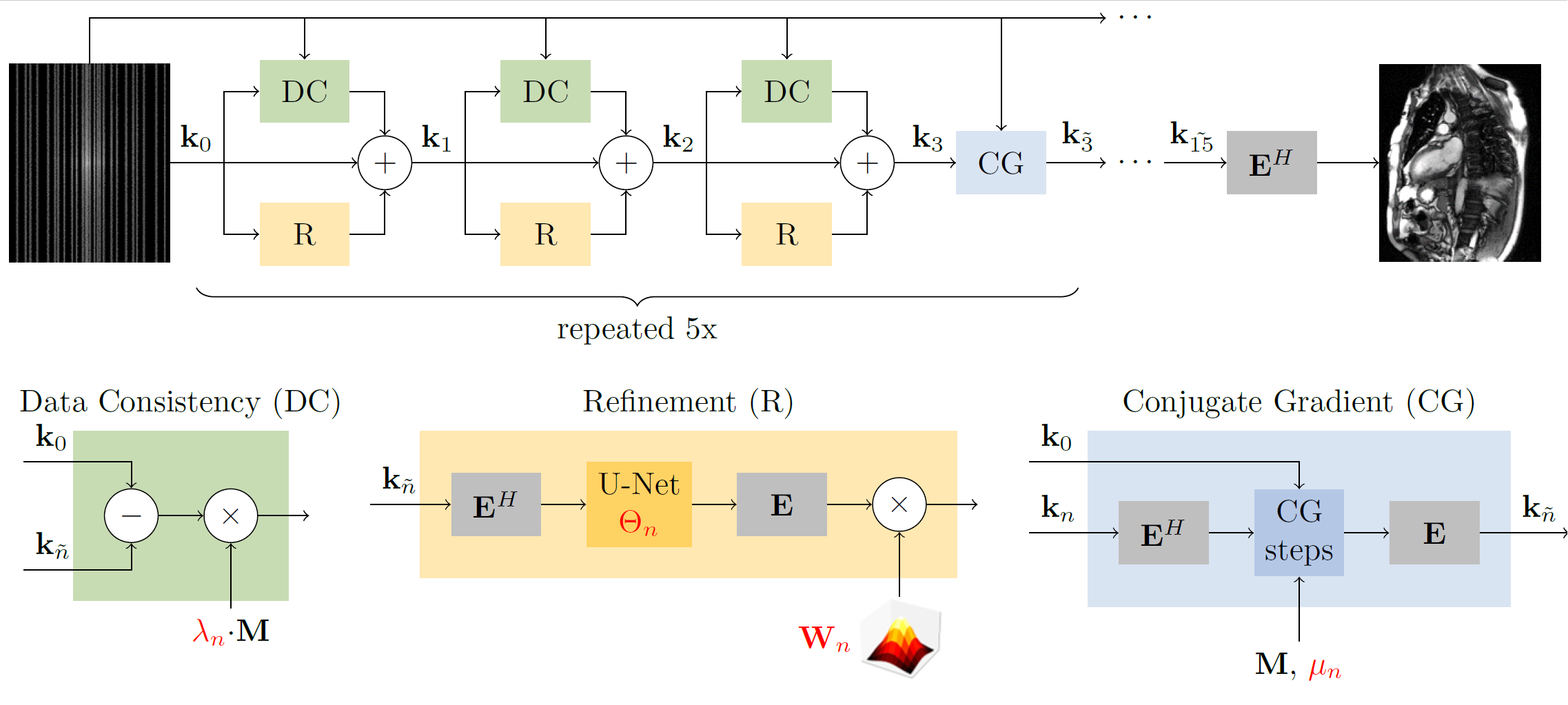
The proposed method is based on a Variational Network architecture adapted for spatiotemporal data and combines it with ideas from conjugate gradient descent.